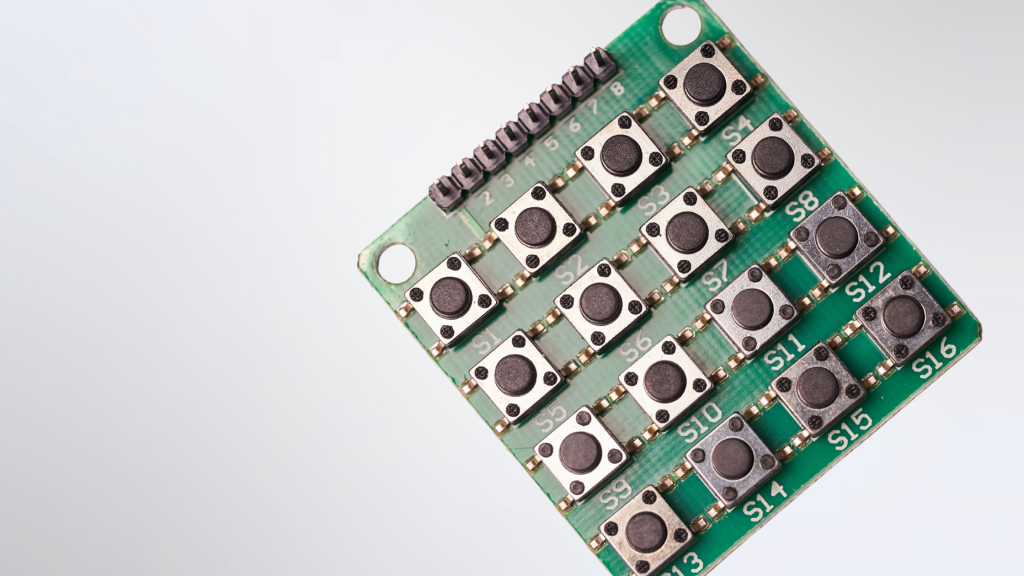
If you’ve ever used an electronic device, chances are you’ve encountered a surface-mount device also known as SMD switches. These tiny components play a crucial role in modern electronics, allowing users to turn devices on and off, adjust settings, and control various functions. However, with so many types of switches on the market, it can be tough to know which is suitable for your project.
SMD switches have revolutionized the world of electronic devices, making them more compact, reliable, and cheaper to produce than ever before. These tiny switches are in various applications, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and more. In this guide, we’ll take a closer look at SMD switches, how they work, and the different types available.
What are SMD Switches?
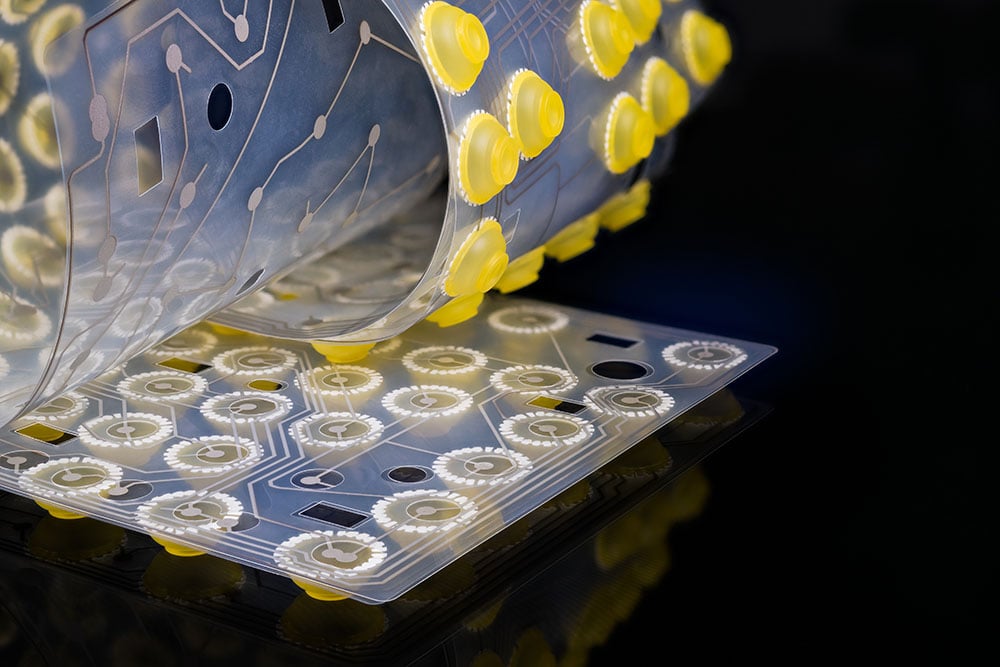
SMD switches are components that allow you to turn a circuit on or off. They are mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB) using surface mount technology (SMT). Eliminating the need for through holes and allowing for greater design flexibility. SMD switches are typically smaller than through-hole switches, making them ideal for compact designs where space is at a premium.
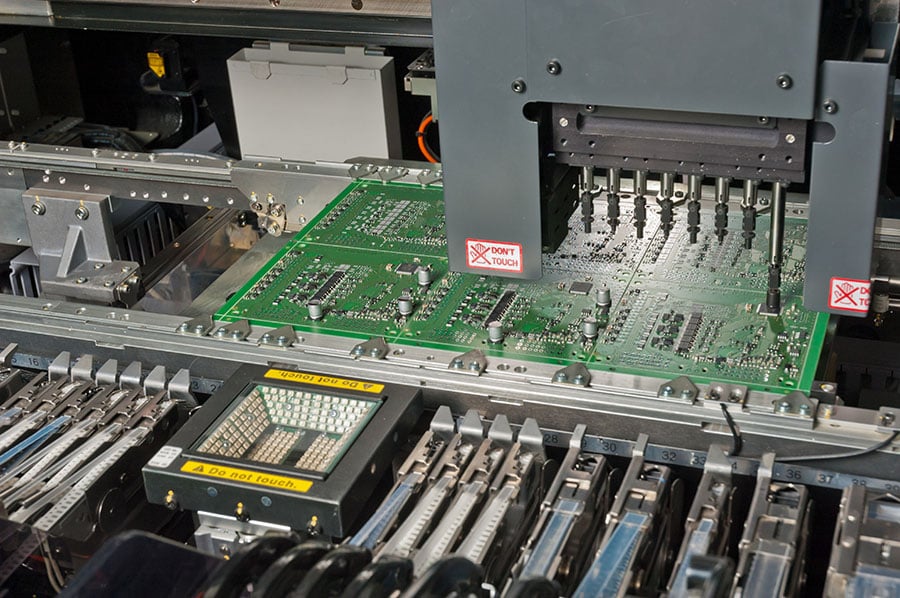
SMT Technology allows you to attach components to a circuit board. The process begins with applying solder paste to the PCB’s surface using a stencil. The solder paste is a mixture of tiny metal balls and flux, which helps the solder adhere to the surface. The SMD components, such as switches, are placed on the PCB using automated pick-and-place machines. The components are aligned and positioned accurately, and then they are soldered to the PCB by heating the solder paste using a reflow oven. The solder melts and flows around the component leads, creating a strong mechanical and electrical connection.
This automated process allows for high-volume manufacturing with consistent quality and accuracy. Additionally, the use of SMT technology allows for the placement of components on both sides of the PCB. Therefore, maximizing space utilization and design flexibility.
How do SMD Switches work?
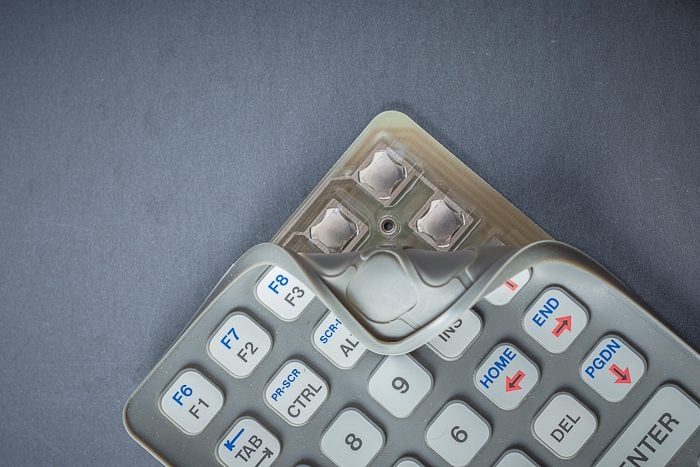
Most SMD switches typically work by using a small metal lever, plunger, or dome to make or break a connection between two metal contacts. When the switch is in the “on” position, the metal lever, plunger, or dome completes the circuit. This allows electricity to flow through the switch. When the switch is in the “off” position, the metal lever, plunger, or dome breaks the circuit—preventing electricity from flowing through the switch. In the case of a dome-style switch, the dome’s feet rest on a circuit pad, and when the center collapses onto that circuit pad, the circuit closes.
Types of SMD Switches
There are many different types of SMD switches available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Here are some of the most common types of SMD switches:
- Tactile Switches: Tactile switches are small, low-profile switches that provide tactile feedback when pressed. Consumer electronics, such as remote and gaming controllers, have tactile switches. They typically come enclosed in a housing and have a “clicky” feel.
- Tactile Dome Switches: Tactile dome switches are small, ultra low-profile switches that provide crisp tactile feedback when pressed. They’re made of stainless steel and can be soldered directly to the circuit board. They have a long life– lasting up to 10 million cycles.
- Slide Switches: Slide switches, also known as DIP switches, are small switches that slide back and forth to turn a circuit on or off. Audio equipment and electronic toys often utilize slide switches.
- Pushbutton Switches: Pushbutton switches are long throw switches that are pressed to turn a circuit on or off. Automotive applications, such as door locks and steering wheel controls, use pushbuttons.
- Rotary Switches: Rotary switches are small, round switches that rotate to select a specific function or setting. Audio equipment and electronic instruments use rotary switches.
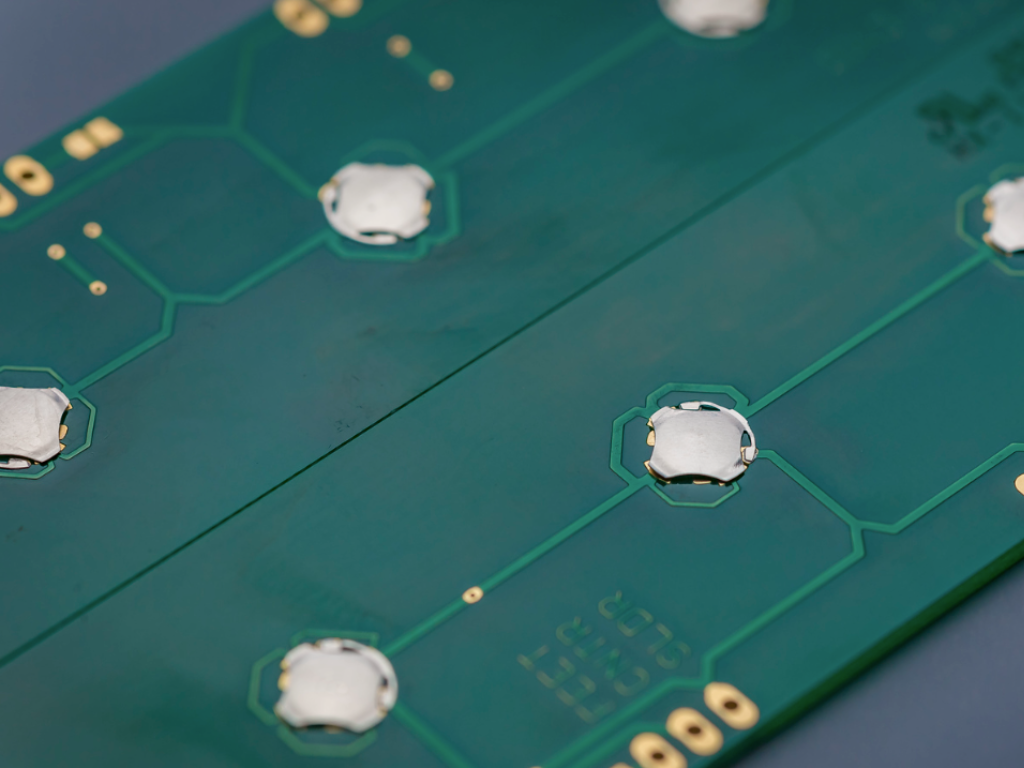
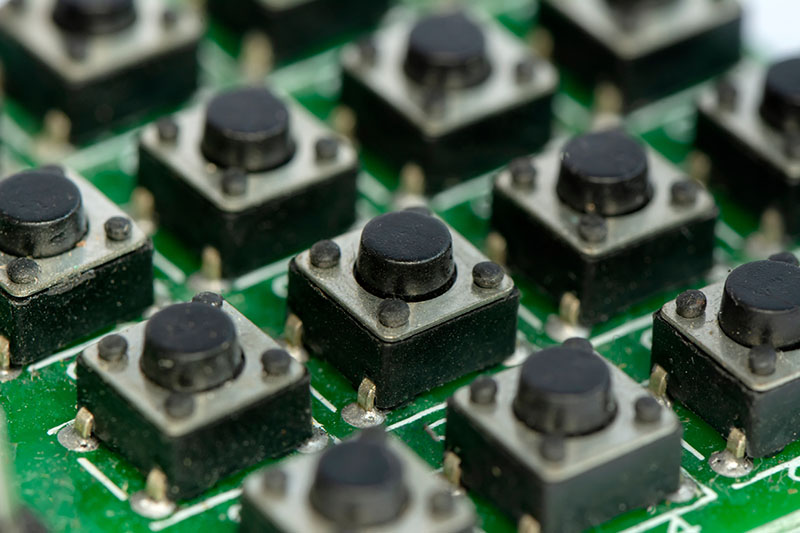
Benefits
The benefits of SMD switches extend beyond their small size and reliability. They also offer cost savings in the manufacturing process. This is because you can assemble them onto a PCB using automated pick-and-place machines. Thus, reducing labor costs and increasing production efficiency.
Additionally, SMD switches are easier to design into applications due to their minimal space requirements. They also have lower parasitic capacitance and inductance than through-hole switches, improving the performance of high-frequency circuits. Overall, the use of SMD switches can result in higher quality and more compact electronic devices that are cost-effective to produce.
Choosing the Right SMD Switch
When choosing an SMD switch, there are several factors to consider, including the type of application, the electrical rating, the life rating, and the size of the switch. It’s important to choose a switch that is appropriate for your specific application to ensure reliable performance.
SMD switches are an essential component of modern electronic devices, providing reliable and compact switching capabilities. With their small size, low profile, and versatile design, they are an ideal solution for a wide range of applications. By understanding the different types of SMD switches and how they work, you can choose the right one for your specific application and ensure reliable performance. Contact Snaptron today for more information on our SMD switch solutions.